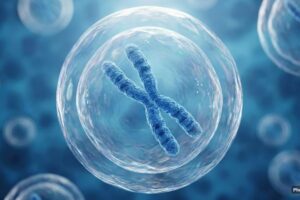
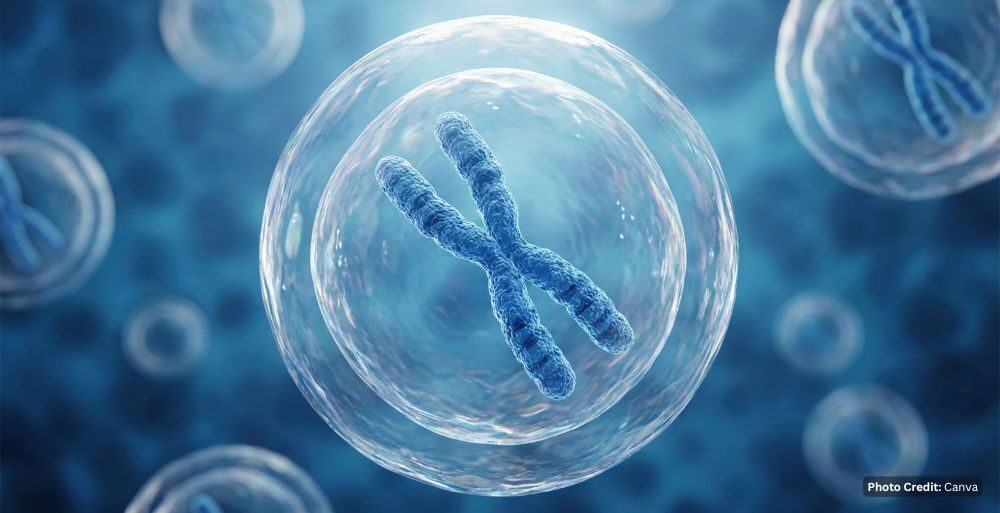
Scientific research has confirmed that a significant percentage of men lose the Y chromosome from their cells as they age, a phenomenon now directly linked to increased mortality and chronic disease. While the Y chromosome was previously dismissed as a \”genetic wasteland\” primarily responsible for sex determination, new evidence indicates its absence triggers systemic health failures. Data shows that 40% of 60-year-old men exhibit this loss, a figure that rises to 57% by age 90.
The condition, known as mosaic loss of Y (mLOY), occurs when the chromosome is misplaced during rapid cell division. Unlike other chromosomes, the Y can be lost without killing the cell, allowing Y-deficient lineages to proliferate throughout the body. Studies involving CRISPR gene-editing and mouse models demonstrate that these Y-less cells drive cardiac fibrosis, leading to heart failure and a significantly shorter lifespan.
Beyond cardiovascular complications, researchers have identified a tenfold higher frequency of Y chromosome loss in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. The genetic degradation is also associated with various cancers, kidney disease, and higher mortality rates from COVID-19. Environmental factors, specifically smoking and exposure to carcinogens, have been identified as primary catalysts that accelerate this chromosomal disappearance.
\”Evidence has mounted over the past few years that when people who have a Y chromosome lose it, the loss is associated with serious diseases throughout the body, contributing to a shorter lifespan.\”
Current findings suggest the Y chromosome plays a critical role in immune system regulation and gene expression that extends far beyond reproductive functions. Scientists are now investigating whether existing anti-fibrotic drugs could mitigate the damage caused by mLOY, potentially bridging the five-year life expectancy gap between men and women.