India’s long and rich history is marked by the rise and fall of several impressive ancient civilizations, each contributing uniquely to the cultural and social fabric of the subcontinent. These societies laid the foundation for what would become one of the world’s oldest continuous civilizations.
The Indus Valley Civilization
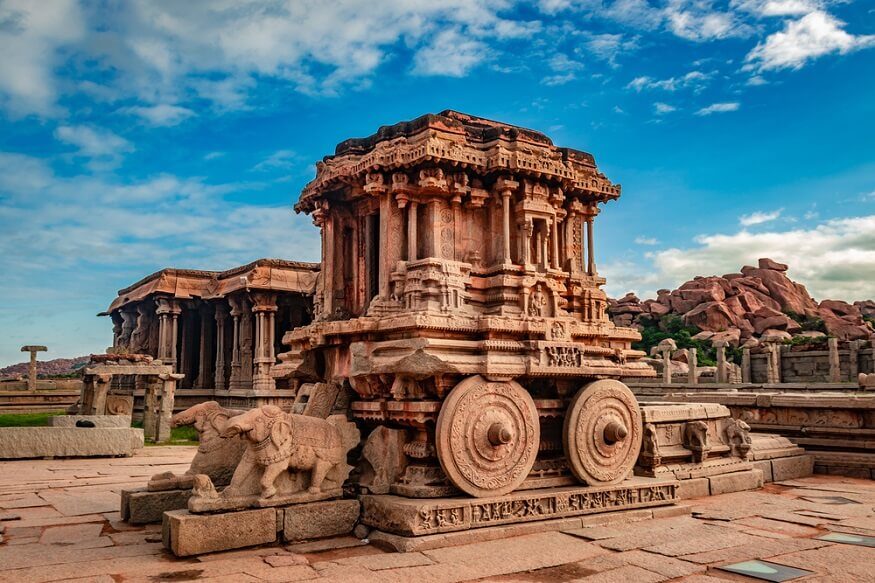
Emerging around 3300 BCE along the fertile floodplains of the Indus River, the Indus Valley Civilization was one of the earliest urban cultures in human history. Known for its sophisticated city planning, advanced drainage systems, and well-built structures like those in Mohenjo-daro and Harappa, this civilization excelled in trade, agriculture, and metallurgy. Despite extensive archaeological findings, the script and detailed cultural practices remain a mystery.
The Vedic Civilization
Following the decline of the Indus cities, the Vedic period (c. 1500–500 BCE) saw the arrival of Indo-Aryan settlers who introduced the Sanskrit language and composed the Vedas—ancient hymns and religious texts forming the basis of Hinduism. This era witnessed the development of early political structures, social stratification through the caste system, and evolving religious ideas that influenced Indian culture profoundly.
The Mahajanapadas
Before the emergence of large empires, India was divided into several powerful kingdoms known as Mahajanapadas around the 6th century BCE. These included Magadha, Kosala, and Vajji, among others. They showcased the growth of urban centers, early governance systems, and philosophical developments such as Buddhism and Jainism.
The Maurya Empire
Founded by Chandragupta Maurya in the 4th century BCE, the Maurya Empire marked the first united political entity across much of India. The reign of Emperor Ashoka stands out for its spread of Buddhism and promotion of ethical governance inspired by non-violence and social welfare.
The Gupta Empire
The Gupta era (circa 320 to 550 CE) is often termed the Golden Age of India due to significant achievements in arts, science, mathematics, and literature. Innovations like the concept of zero, classical Sanskrit literature by Kalidasa, and the construction of stunning temples define this culturally rich period.
The Sangam Civilization
In South India, the Sangam period flourished between 300 BCE and 300 CE, known for its Tamil literature and flourishing trade networks across the Indian Ocean. It contributed significantly to the cultural and literary heritage distinct from northern Indian civilizations.