The year 2025 marked one of the most significant periods of change in U.S. immigration policy in recent decades, affecting how people travel to the United States, obtain work visas, apply for permanent residency, and pursue citizenship. A series of regulatory updates and executive actions introduced by the Trump administration reshaped key immigration pathways, drawing strong reactions from employers, civil rights groups, and foreign nationals.
Below are five of the most impactful immigration changes implemented in 2025.

H-1B Visa Overhaul Targets Wages and Skill Levels
The Department of Homeland Security unveiled a major proposal in September to revamp the H-1B visa program, a cornerstone of the U.S. technology and innovation economy. The program allows American companies to hire highly skilled foreign professionals, including software engineers, data scientists, and researchers.
Under the new framework, employers are encouraged to prioritize higher-paying roles or positions requiring advanced and specialized skills. The changes followed a proclamation by Donald Trump introducing a $100,000 fee for H-1B visa applications. The rule, published in the Federal Register, is scheduled to take effect in February 2026.
According to DHS, the overhaul aims to “better protect the wages, working conditions, and job opportunities for American workers.” A spokesperson for U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services stated that the previous random lottery system had been “exploited by employers seeking lower-cost foreign labor.”
Expanded Facial Recognition for Non-Citizens at U.S. Borders
On December 26, 2025, DHS implemented a rule expanding the use of facial recognition technology for non-citizens entering and exiting the United States. The regulation authorizes U.S. Customs and Border Protection to collect facial biometrics at airports, land borders, seaports, and other approved departure points.
The rule applies to green card holders and other legally residing non-U.S. citizens. While U.S. citizens are not required to participate, DHS noted they may continue to do so voluntarily. Officials said the expanded biometric system enhances identity verification and border security while streamlining travel processes.
Social Media Screening for Foreign Tourists
In another major shift, DHS moved toward mandatory social media screening for foreign travelers entering the U.S. under the Visa Waiver Program. A December notice in the Federal Register announced that Electronic System for Travel Authorization (ESTA) applicants must now disclose their social media activity from the past five years.
The change aligns with Executive Order 14161, issued in January 2025, which focuses on protecting the U.S. from foreign terrorist threats and public safety risks. DHS described ESTA as an automated system used to assess eligibility and security risks before travel authorization is granted.
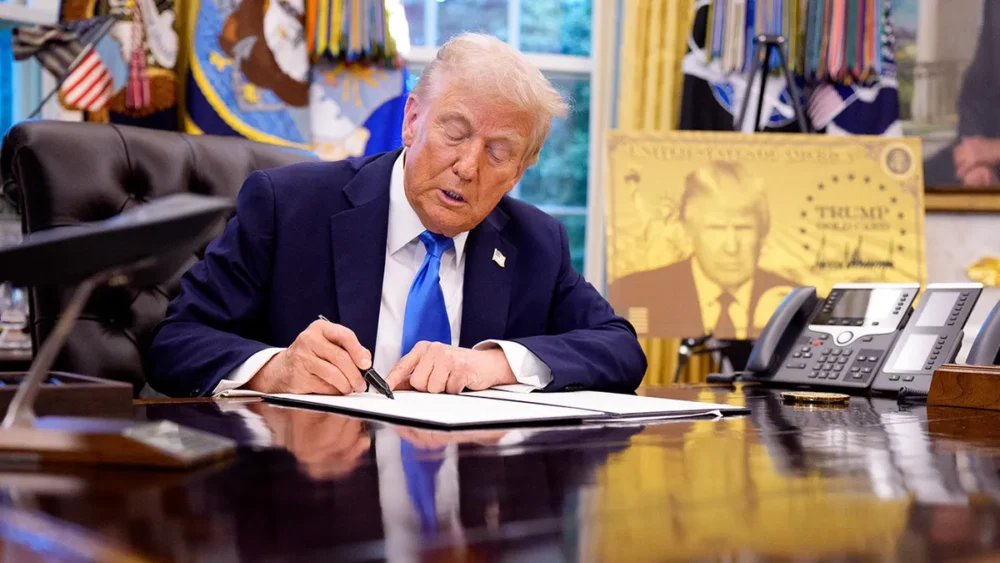
Trump Introduces $1 Million “Gold Card” Residency Program
In December, President Trump announced the launch of the “Trump Gold Card,” a new, high-value immigration initiative offering a fast-tracked path to U.S. permanent residency. Priced at $1 million, the card features Trump’s portrait, the Statue of Liberty, and the American flag on a gold background.
Applicants can apply via the official website, trumpcard.gov, where submission of documents and a non-refundable processing fee triggers an accelerated review by USCIS. Approved applicants receive lawful permanent resident status, classified under EB-1 or EB-2 visa categories.
Trump claimed the program could generate over $100 billion, stating the funds would be used for tax reductions, growth initiatives, and debt reduction.
Revamped U.S. Citizenship Test Raises the Bar
A new version of the U.S. naturalization civics test went into effect in 2025, significantly increasing its difficulty. Applicants must now answer 20 oral questions, up from 10 previously, drawn from a list of 128 questions. To pass, applicants must answer at least 12 questions correctly.
The revised test removes geography questions and requires applicants to identify all three branches of government, rather than just one. USCIS said the changes ensure that new citizens possess a deeper understanding of U.S. civics and democratic values.
USCIS spokesperson Matthew Tragesser described American citizenship as “the most sacred citizenship in the world,” adding that the updated test ensures new citizens are fully assimilated and prepared to contribute meaningfully to the nation.
A Transformative Year for U.S. Immigration
Together, these policy shifts reflect a broader recalibration of U.S. immigration priorities—emphasizing security, economic value, assimilation, and enforcement. As these changes take effect in 2026, they are expected to have far-reaching implications for students, professionals, tourists, investors, and aspiring citizens worldwide.